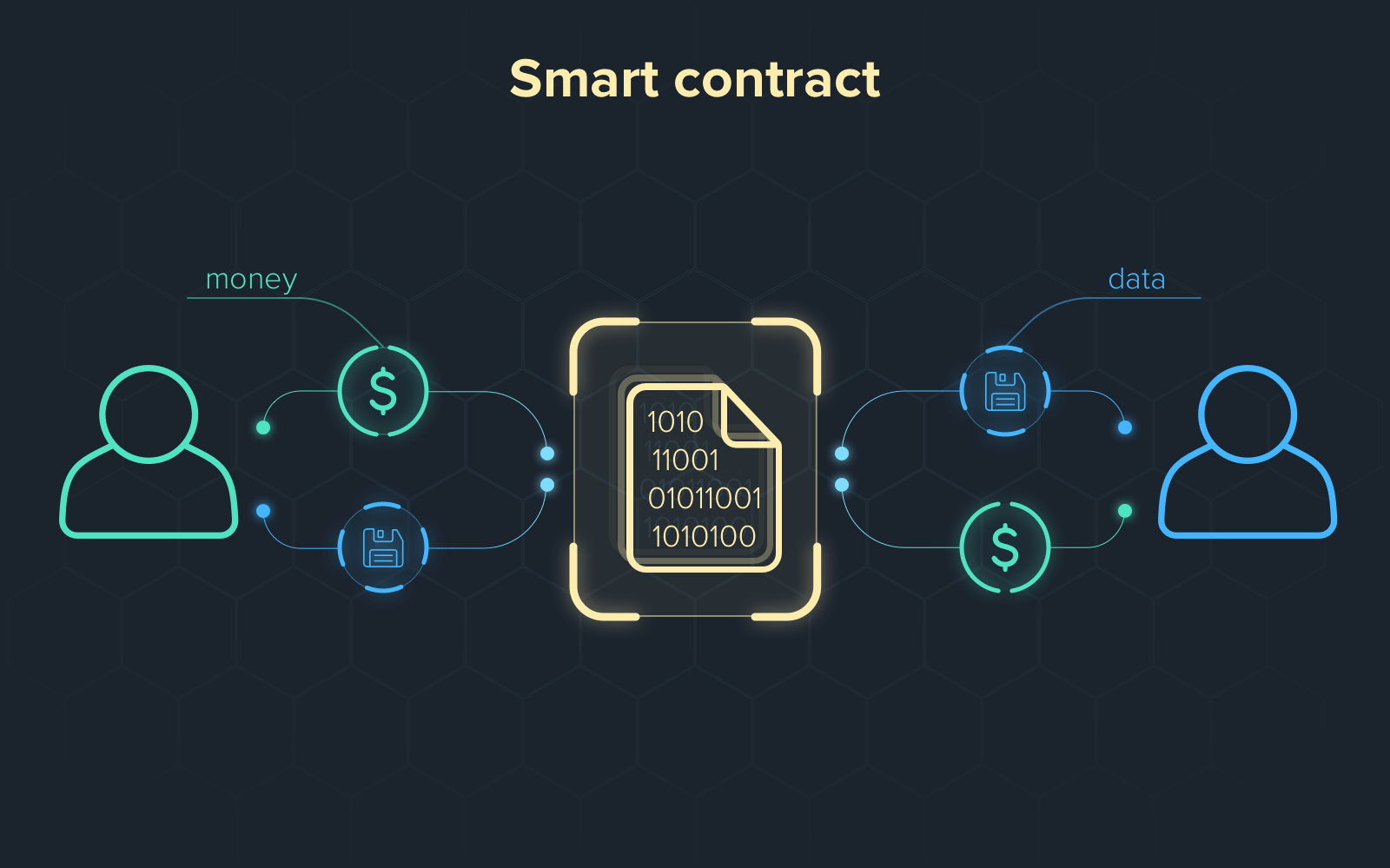
In the evolving landscape of blockchain technology, smart contracts have emerged as a pivotal innovation, enabling automated and trustless transactions. These self-executing contracts are encoded with predefined rules and conditions, allowing them to operate without intermediaries. This article delves into the concept of smart contracts, their functionality, benefits, and diverse applications.
Understanding Smart Contracts
A smart contract is a computer program or transaction protocol that automatically executes, controls, or documents events and actions according to the terms of a contract or agreement. The primary objectives of smart contracts are to reduce the need for trusted intermediaries, minimize arbitration costs, and mitigate fraud losses.
According to Wikipedia, the concept was first proposed by computer scientist Nick Szabo in 1996, who likened smart contracts to vending machines: users input a value, and in return, receive a product or service without the need for a middleman.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
Smart contracts operate on blockchain networks, ensuring transparency and security. Their operation involves several key steps:
- Agreement Encoding: The terms of the contract are translated into code, defining the conditions under which the contract will execute.
- Deployment: This code is deployed onto a blockchain, becoming an immutable part of the network.
- Triggering Events: When predefined conditions are met (e.g., receiving a specific amount of cryptocurrency), the smart contract automatically executes the corresponding actions.
- Execution and Verification: The blockchain’s decentralized network of nodes verifies the transaction, ensuring that all conditions have been satisfied before execution.
For instance, consider a crowdfunding campaign implemented via a smart contract:
- If the funding goal is reached by a certain date, the collected funds are released to the project initiator.
- If the goal is not met, the funds are automatically refunded to the contributors.
This process eliminates the need for a central authority to manage the funds.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts offer numerous advantages over traditional contractual agreements:
- Trust and Transparency: All parties have access to the contract’s terms and execution records on the blockchain, ensuring openness.
- Security: Cryptographic encryption secures the contract, making it tamper-resistant.
- Efficiency: Automation reduces the time and cost associated with manual processing and intermediaries.
- Accuracy: Eliminates errors that can occur in manual contract execution.
Applications of Smart Contracts
The versatility of smart contracts enables their application across various industries:
- Finance: Facilitating decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, including lending, borrowing, and trading platforms.
- Supply Chain Management: Tracking the provenance of goods, ensuring authenticity, and automating payments upon delivery.
- Real Estate: Automating property transfers and rental agreements, reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Healthcare: Managing patient consent and securely sharing medical records among authorized providers.
- Legal Industry: Streamlining contract execution and enforcement, reducing reliance on traditional legal processes.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their potential, smart contracts are not without challenges:
- Immutability: Once deployed, altering a smart contract is challenging, making it crucial to ensure the code is free from bugs and vulnerabilities.
- Legal Recognition: The legal status of smart contracts varies across jurisdictions, and they may not be recognized as legally binding in some areas.
- Security Risks: Vulnerabilities in smart contract code can be exploited, leading to significant financial losses.
- Scalability: Executing complex smart contracts can be resource-intensive, posing scalability issues on certain blockchain networks.
Conclusion
Smart contracts represent a transformative shift in how agreements are formed and executed, leveraging blockchain technology to enable automated, transparent, and secure transactions. As the technology matures and legal frameworks evolve, smart contracts are poised to play an increasingly integral role in various sectors, driving efficiency and innovation.